This page is not sourced from the book, but is directly from a handout for CMPA by Ma’am Dang. I believe this is a topic found in Maglaya’s Community Nursing book, which I am not in possession of.
Demography is the study of the size, territorial distribution, and composition of population and the changes therein (Duncan & Hauser, 1972). Literally translated from Greek, it means “description of the people”. A Population is defined as group of individuals of the same species living and interbreeding within a given area. There are several general parameters in studying the population:
- Population Size: the number of people in a given place at a given time.
- Population Distribution: the specific geographic location of the population.
- Population Composition: the characteristics of population as to age, sex, occupation, or educational level.
- Population Projection: a common demographic tool that provides a basis for other statistical projections. It helps governments with decision-making.
There are three components that affect population growth:
flowchart LR
A(Birth)
B(Death)
C(Migration)
A---B
B---C
Sources of Data
- Census: conducted by a national government and attempts to enumerate every person in a country. It may be done in two ways:
- De Jure: individuals are recorded based on legal residence
- De Facto: individuals are recorded based on their location at a specific time.
- Sample Survey: data gathered from a subset of the population proportionate to the general population.
- Registration System: deals with recording of vital events such as birth, marriage, and death.
Demography Statistics
- Natural Increase: the difference between live births and deaths in a specified period of time.
- Rate of Natural Increase: the difference between live births and deaths in a specified period of time. Refer to Epidemiology for the discussion on crude birth and death rates.
- Absolute Increase per Year: the number of people that are added to the population per year. is the population size and is the population size from years before.
- Relative Increase (Population Growth Rate): the actual differences between the two census counts expressed in percent relative to the population size made during an earlier census. This percent is the average yearly percentage change over the same time frame.
Population Composition
- Sex Composition (Sex Ratio): the ratio of males to females in a population, expressed as “number of males for every 100 females”.
- Age Composition (or distribution): the proportionate number of persons in successive age categories in a given population. As an example, a population with persistently high fertility would exhibit a large proportion of children, and a small proportion of aged persons.
- Median Age: the age that divides a population into two numerically equally sized groups, i.e., exactly half the population would be younger or older than the median age. It is a single age that summarizes the age distribution of a population.
- Dependency Ratio: the age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force and those typically in the labor force. This age group is between 15 years old and 64 years old. It is used to measure the pressure on the productive population to support the dependent population. It is expressed as a percent, e.g., “60% of the population is dependent on the remaining 40%”
- Age and Sex Composition: a population pyramid that depicts both age (vertical axis) and sex (horizontal axis). The shape of this pyramid can determine the pattern of population change. A normal pyramid (as illustrated below) shows rapid growth, a thin, almost columnar pyramid shows slow growth, and a top-heavy pyramid shows negative growth.
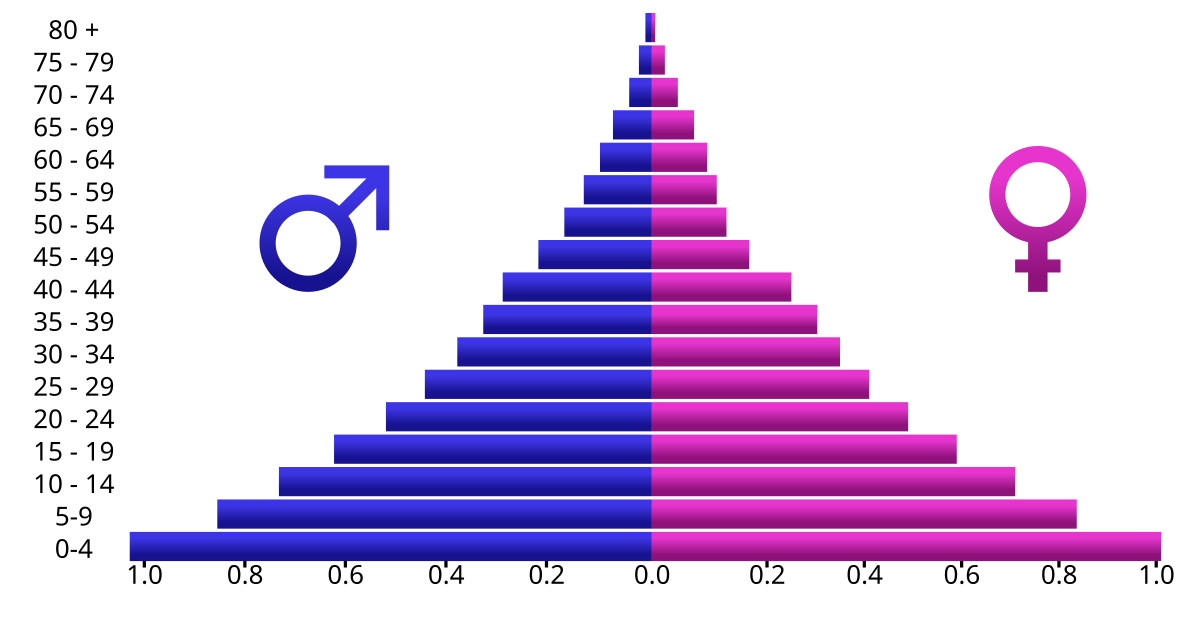
Population Distribution
The pattern of where people live. It denotes the spatial pattern: due to dispersal of population, formation of agglomeration (groups), and linear spread.
- Urban-Rural Distribution: illustrates the proportion of the people living in urban areas compared to rural areas.
- Crowding Index: an alternative measure of household crowding. It is defined as the number of usual residents in a dwelling divided by the number of rooms in the dwelling.
- Population Density: is calculated as population divided by total land area, expressed as number of people per square kilometer of land area.